- :+91 - 89402 62058, +91 76392 89213
- Agilkarai Street, Tirumayam, Tamil Nadu 622507
Medications for Neurological Disorders
Medications for neurological disorders aim to manage symptoms and improve patients' quality of life. Antiepileptic drugs, like phenytoin or levetiracetam, help control seizures in epilepsy. Dopamine agonists, such as levodopa, are used to alleviate motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease. Medications like memantine or donepezil may be prescribed for cognitive symptoms in Alzheimer's disease. Anti-migraine drugs, including sumatriptan, are used to relieve migraine headaches.
Stroke Treatment
Stroke treatment is time-sensitive and varies based on the type of stroke. For ischemic strokes, the administration of clot-busting drugs like alteplase can help restore blood flow. Mechanical thrombectomy may be performed to remove clots from large vessels. In hemorrhagic strokes, interventions aim to control bleeding and reduce pressure on the brain. Rehabilitation, including physical and occupational therapy, is crucial for recovery post-stroke.
Epilepsy Management
Epilepsy management involves a tailored approach to control seizures and enhance quality of life. Antiepileptic medications, such as carbamazepine or valproate, are often prescribed. Regular monitoring of drug levels and potential side effects is crucial. In some cases, surgical interventions may be considered to control seizures. Collaborating closely with neurologists and following individualized treatment plans contribute to effective epilepsy management.
Movement Disorders
Movement disorders encompass conditions affecting body movements, often involving disruptions in the nervous system. Parkinson's disease, characterized by tremors and bradykinesia, is a common movement disorder. Essential tremor causes involuntary shaking, while dystonia results in sustained muscle contractions. Huntington's disease leads to progressive motor dysfunction and cognitive decline. Treatment may involve medications, physical therapy, and, in specific cases, surgical interventions.
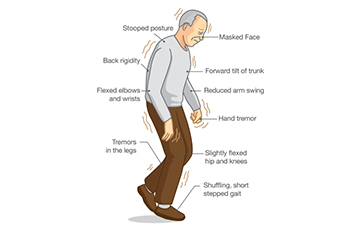
Neuromuscular disorders
The treatment of neuromuscular disorders involves addressing underlying causes and managing symptoms to enhance quality of life. For conditions like muscular dystrophy, corticosteroids or gene therapy may be considered. Physical therapy and assistive devices play a crucial role in maintaining mobility and function. Medications, such as immunosuppressants, are prescribed for disorders like myasthenia gravis. Collaborating with neurologists and a multidisciplinary healthcare team ensures a comprehensive and tailored approach to managing neuromuscular disorders.
Migraine and headache management
Migraine and headache management involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medications. Identifying triggers, such as certain foods or stress, helps in prevention. Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or NSAIDs may be used for mild headaches, while prescription medications like triptans are effective for migraines.
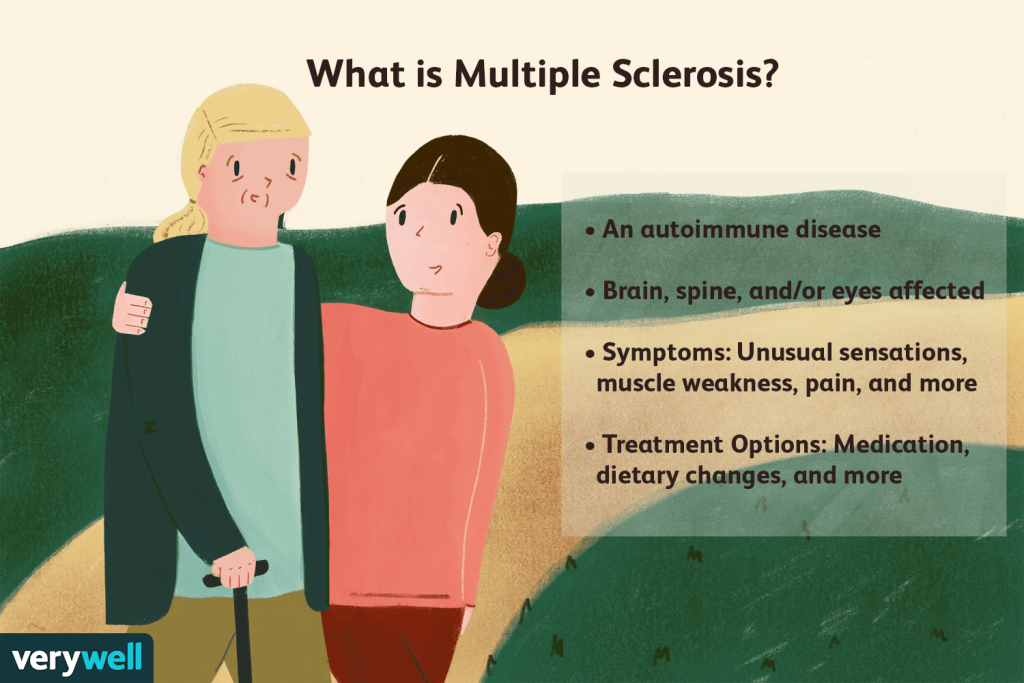
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Treatment
Multiple sclerosis (MS) treatment aims to manage symptoms and slow disease progression. Disease-modifying therapies, such as interferons or oral medications, help modulate the immune system and reduce relapses. Symptomatic treatment may include medications for spasticity, fatigue, and pain. Physical and occupational therapy contribute to improving mobility and daily functioning.
Alzheimer's Disease and Dementia Management
Alzheimer's disease and dementia management involve a holistic approach to enhance cognitive function and quality of life. Medications like cholinesterase inhibitors may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms. Supportive therapies, including cognitive stimulation and reminiscence therapy, contribute to overall care. Creating a structured environment and providing caregiver support are crucial aspects of management.
Head and Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation
Head and spinal cord injury rehabilitation focuses on restoring function and improving quality of life after trauma. Multidisciplinary teams, including physical therapists and occupational therapists, tailor rehabilitation plans to individual needs. Interventions may include mobility training, adaptive equipment use, and cognitive therapy. Psychological support is crucial for emotional well-being during the recovery process. Regular follow-ups and collaboration with rehabilitation specialists are essential for optimizing outcomes in head and spinal cord injury rehabilitation.